
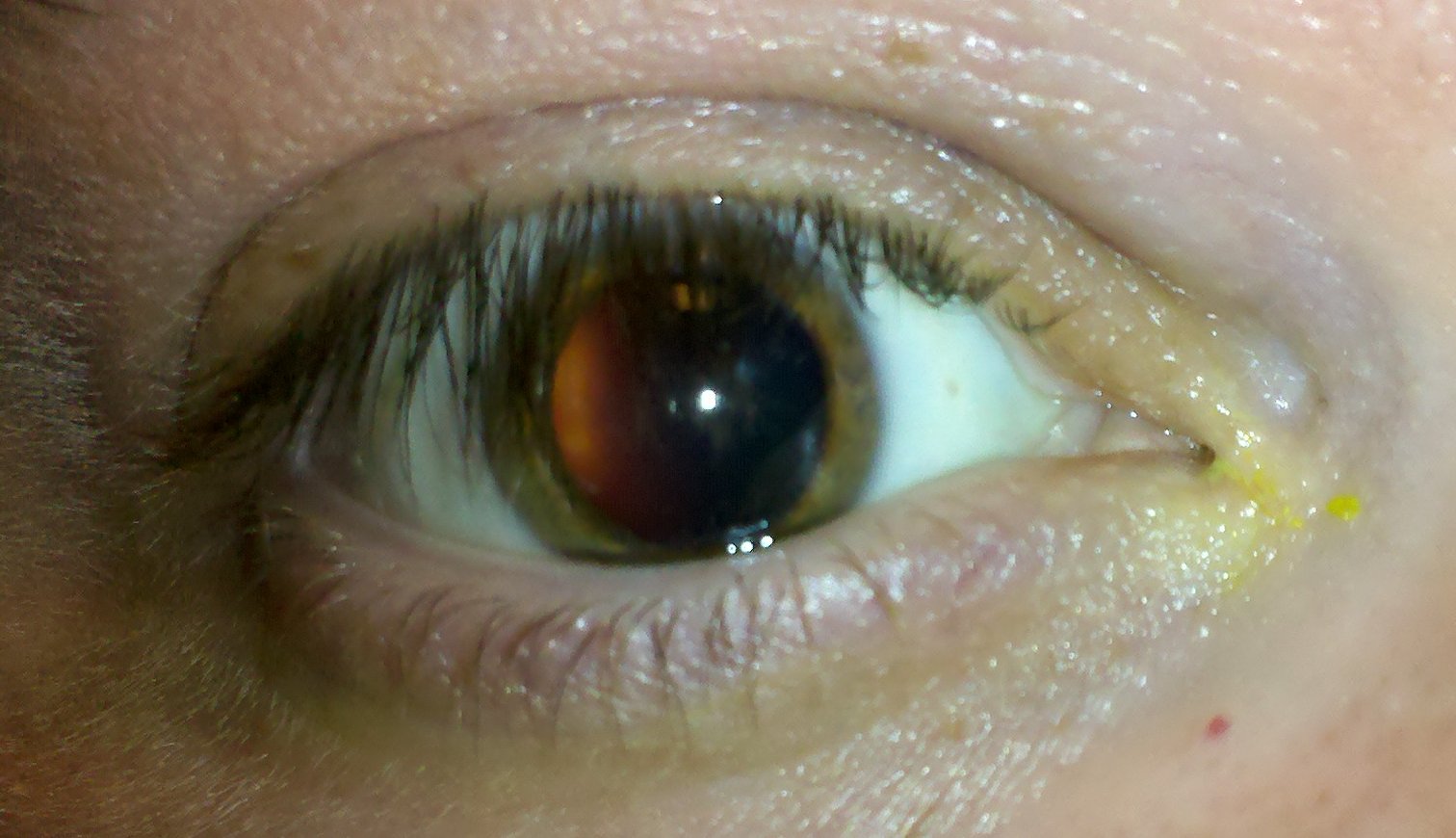
HistoryĪACG symptoms tend to develop over hours to days. Topiramate use has been associated with bilateral AACG.ĪACG is an important differential diagnosis to consider in any patient presenting with a painful red eye. oxybutynin), antidepressants (SSRIs and TCAs) or pupil-dilating drops (e.g. Pupil mid-dilation can be caused by being in a dark room or the use of certain medications such as anticholinergics (e.g. Pupil mid-dilation can cause AACG by precipitating pupillary block in those at risk. Anatomical predisposition: including short eyeball length and hypermetropia (longsightedness).Female sex: women have a three times greater risk than men.Increasing age: particularly 6 th to 7 th decade of life.This causes the peripheral iris to bow forward blocking the drainage angle, with subsequent rapid rise in IOP. This is mediated by a ‘ pupillary block’ – contact between the iris and the lens when the iris is in a mid-dilated position. In AACG, there is reduced drainage of aqueous humour due to anterior chamber angle narrowing from irido-trabecular contact.
The vast majority of these individuals do not experience angle closure attacks and the risk is small at 1 in 1000 per year. 2 PathophysiologyĪACG occurs in anatomically pre-disposed individuals with shorter eye lengths and shallower anterior chambers. The normal intraocular pressure (IOP) is maintained between 11-21mmHg. It is produced by the ciliary body and travels through the pupil into the anterior chamber (the area between the iris and cornea).Īqueous humour drains out of the anterior chamber through the trabecular meshwork and flows into the canal of Schlemm (Figure 1). The aqueous humour supplies nutrients to the cornea and lens. You might also be interested in our medical flashcard collection which contains over 1000 flashcards that cover key medical topics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
